Intraoperative CT (ICT) Guided Endoscopic Third Ventricular Cyst Excision
Image guided surgery is one of the most significant advances in Neurosurgery and enables locating the target lesion and monitor resection by avoiding disruption of hazardous areas. Neuronavigation has drawback of failing accuracy with brain shift as surgery proceeds. If preoperative images are acquired few days prior to surgery then few lesions may change in size in this course of time and may not reflect real time data. Intraoperative imaging update of navigational data gives more accurate information about current pathology status and resection progress.
Colloid cyst is a pedunculated pathological cyst of third ventricle and disturbs the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid and can cause acute obstruction of the third ventricle resulting in acute hydrocephalus, brain herniation, coma, and death.
This obstruction is usually intermittent and ventriculomegaly may be of variable size. Intraoperative CT before surgery may be better imaging than preoperative CT scan for seeing ventricular size and trajectory planning.
A 25 years old male was presented in emergency with headache for last 3 days and now severe headache with vomiting for last one hour. On examination he was slightly confused and had papilledema.
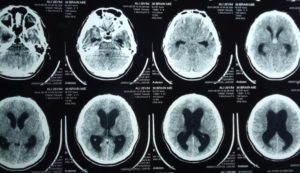
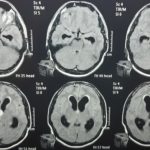
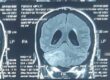
His CT scan Brain showed hyperdense third ventricular colloid cyst and biventricular hydrocephalus.
MRI Brain showed Isointense on T1 and hyperintense on T2 third ventricular colloid cyst with hydrocephalus.
Endoscopic Colloid Cyst excision was planned.
Peroperative before surgery CT scan Brain was acquired after anesthetization of patient and head clamping with head holder. That imaging data was loaded in Neuronavigation Station and trajectory planning was performed.
Burr Hole site was marked at planned site. Navigation guided ventricular puncture was done.
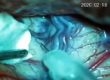
Colloid cyst wall cautrised, incised and jelly like material was sucked. Cyst wall was excised as one piece. Hemostasis was secured with copious irrigation.
Ventricular drain was placed.
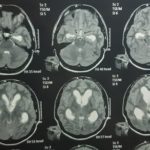
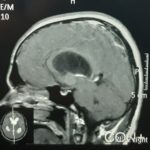
Peroperative CT Scan Brain was acquired after procedure to assess degree of resection, intraventricular clot and drain position.